Unlock GABA: The Key to a Calm, Balanced Brain!
Feeling overwhelmed? Many people find themselves searching for natural ways to manage stress and anxiety, and understanding GABA might be the answer. The gaba function neurotransmitter plays a vital role in calming the nervous system, much like a brake pedal for your brain. Indeed, Experts at the National Institute of Mental Health research the gaba function neurotransmitter impacts mood regulation. Strategies such as mindfulness meditation often enhance GABA activity, contributing to a sense of peace. Similarly, Certain supplements like L-Theanine may support gaba function neurotransmitter levels, promoting relaxation without drowsiness.

Image taken from the YouTube channel Neuroscientifically Challenged , from the video titled 2-Minute Neuroscience: GABA .
Unlock GABA: The Key to a Calm, Balanced Brain!
Do you find yourself constantly battling racing thoughts, a relentless sense of unease, or the frustrating inability to switch off at night? These experiences, unfortunately, are becoming increasingly common in our fast-paced, hyper-connected world. The feeling of being perpetually overwhelmed has almost become the new normal.
But what if there was a natural key to unlocking a sense of calm, a way to restore balance to your overstimulated mind?
Enter GABA, your brain's primary inhibitory neurotransmitter, a powerful agent responsible for taming the flames of anxiety and promoting restful sleep. Think of GABA as the brain's natural "off switch," helping to quiet the neuronal chatter that contributes to stress and sleeplessness.
Understanding GABA's Role
GABA, or gamma-aminobutyric acid, is a naturally occurring amino acid that acts as a chemical messenger in the brain.
Its primary role is to reduce the excitability of neurons, effectively slowing down nerve impulses and preventing overstimulation. This inhibitory action is crucial for maintaining a healthy balance within the nervous system. Without sufficient GABA, the brain can become overloaded, leading to a cascade of negative effects.
Why This Matters
This article is your guide to understanding the crucial role GABA plays in your mental and physical well-being. We'll explore the science behind GABA, its profound impact on everything from anxiety levels to sleep quality, and the practical steps you can take to naturally support healthy GABA levels in your brain.
Your Journey to a Calmer Mind Starts Here
Consider this your starting point for understanding and nurturing your brain's natural calming mechanisms. By learning about GABA and how to support its function, you can take control of your mental well-being and unlock a greater sense of peace and balance in your life.
Your Journey to a Calmer Mind Starts... now, with a deeper understanding of exactly what GABA is and how it functions as a pivotal player in the intricate workings of your nervous system. Let's peel back the layers of this essential neurotransmitter, exploring its fundamental nature and mechanism of action within the brain.
Decoding GABA: The Brain's Natural Calming Agent
At the heart of our brain's ability to maintain equilibrium lies a delicate balance between excitation and inhibition. GABA is a crucial component of this balance, acting as the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter that counteracts the effects of its excitatory counterpart. Understanding GABA's role is paramount to appreciating its impact on our mental and physical well-being.
What is GABA?
GABA, or gamma-aminobutyric acid, is the chief inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system (CNS), which includes the brain and spinal cord. It's a naturally occurring amino acid that works to reduce neuronal excitability throughout the nervous system.
Think of your brain as a bustling city, filled with countless messages constantly being sent and received. GABA acts like the traffic control system, preventing the city from descending into chaos.
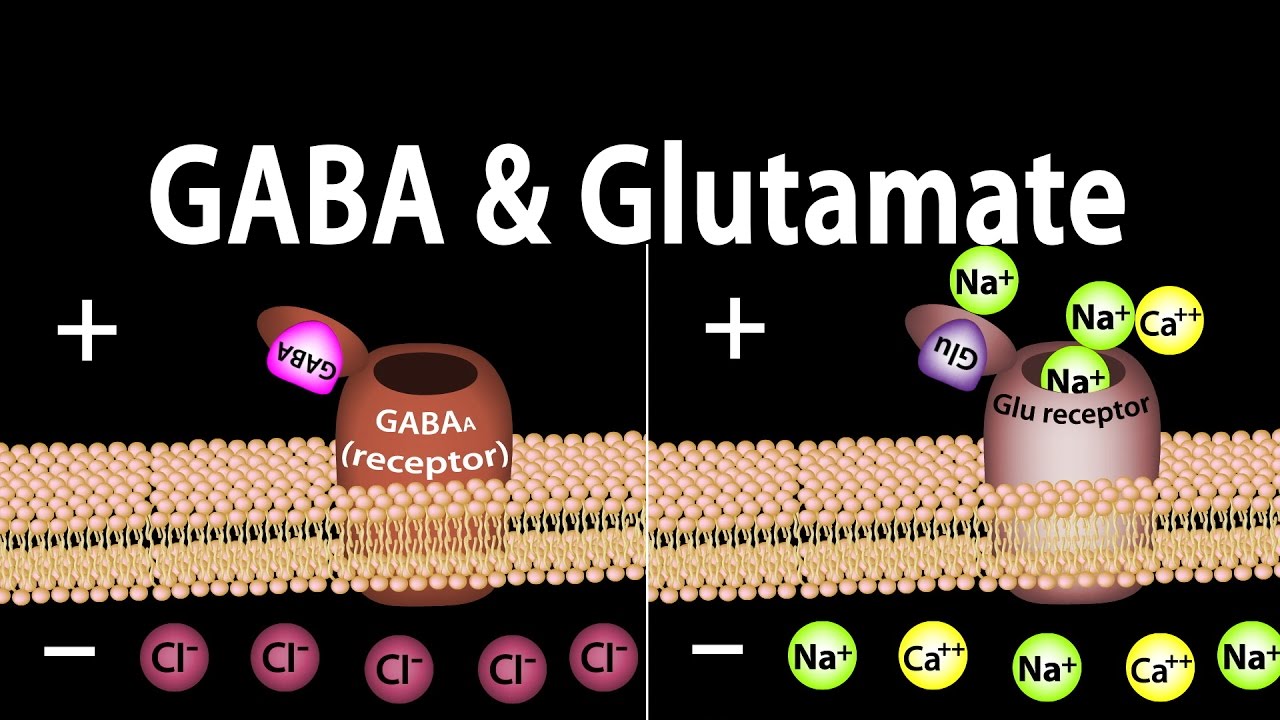
The Balance with Glutamate
While GABA puts the brakes on neuronal activity, Glutamate is the primary excitatory neurotransmitter, accelerating brain activity. Glutamate is vital for learning, memory, and overall cognitive function.
However, too much Glutamate without sufficient GABA to balance it can lead to overstimulation, anxiety, and even seizures. The harmonious interplay between GABA and Glutamate is, therefore, essential for optimal brain function. It's the Ying and Yang of the brain, constantly working to maintain a state of equilibrium.
How Does GABA Work?
GABA's mechanism of action is elegantly simple, yet profoundly effective. It involves a series of steps that ultimately lead to the inhibition of neuronal firing.
GABA Release and Receptor Binding
When a neuron needs to quiet down the activity of another neuron, it releases GABA into the synaptic cleft – the space between the two neurons.
This released GABA then diffuses across the cleft and binds to specific receptors on the receiving neuron. These receptors are primarily of three types: GABA-A, GABA-B, and GABA-C.
When GABA binds to these receptors, it triggers a change in the receiving neuron, making it less likely to fire an electrical signal. This is achieved by allowing negatively charged chloride ions to enter the neuron, which reduces its overall excitability.
GABAergic Neurons and Action Potential
Neurons that produce and release GABA are called GABAergic neurons. These specialized cells are strategically located throughout the brain and spinal cord, allowing them to exert widespread inhibitory influence.
To further understand how GABA works to calm the brain, it's important to understand the concept of Action Potential.
When a neuron reaches a certain threshold of excitation, it fires an electrical signal known as an action potential. This signal travels down the neuron's axon, ultimately leading to the release of neurotransmitters that can stimulate or inhibit the next neuron in the chain.
GABA inhibits neurons, reducing the likelihood of them reaching the threshold needed to fire an action potential. This action prevents the overstimulation of the nervous system and promotes a sense of calm.
In essence, GABA works to maintain harmony within the brain by ensuring that neuronal excitation doesn't spiral out of control. This inhibitory action is indispensable for managing anxiety, promoting restful sleep, and overall maintaining mental and physical well-being.
Decoding GABA’s role offers a glimpse into the intricate communication network within our minds, a network where balance is paramount. The dance between excitation and inhibition, governed largely by Glutamate and GABA respectively, dictates the rhythm of our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. Now, let's delve deeper into the specific ways GABA impacts our well-being, exploring its crucial roles in regulating anxiety, promoting restful sleep, and its involvement in various other health conditions.
The Crucial Roles of GABA in Brain Function and Overall Well-being
GABA isn't just some obscure brain chemical; it's a key player in maintaining mental and physical equilibrium. Its influence spans across various critical functions, and understanding these roles is vital for appreciating its importance. Imbalances in GABA levels can manifest in a variety of ways, impacting everything from our mood to our sleep patterns.
GABA and Anxiety
Anxiety, a prevalent condition in today's fast-paced world, is often linked to an imbalance in neurotransmitter activity. Insufficient GABA can leave the nervous system in a state of heightened excitability, making individuals more susceptible to feelings of anxiety and panic.
Think of GABA as a natural brake on the brain's stress response. When GABA levels are low, this brake becomes less effective, leading to a racing mind, physical tension, and overwhelming feelings of unease.
The Role of GABA in Regulating Fear Responses
GABA plays a crucial role in modulating the amygdala, the brain's center for processing emotions, particularly fear. When faced with a perceived threat, the amygdala activates the body's fight-or-flight response.
GABA helps to keep this response in check, preventing it from becoming excessive or prolonged. In situations where GABA is deficient, the fear response can become amplified, leading to anxiety disorders like phobias or panic attacks. Essentially, GABA helps to ensure the amygdala doesn’t send out false alarms.
GABA and Sleep
Sleep is a fundamental pillar of health, and GABA plays a critical role in its regulation. As the brain's primary inhibitory neurotransmitter, GABA promotes relaxation and reduces neuronal excitability, paving the way for a restful night's sleep.
By quieting the chatter of the mind, GABA allows us to transition from wakefulness to sleep more easily. It also helps to maintain a state of deep, restorative sleep throughout the night.
The Consequences of Low GABA on Sleep
When GABA levels are insufficient, the brain can remain in a state of hyperarousal, making it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep. This can manifest as insomnia, characterized by difficulty initiating sleep, frequent awakenings during the night, or waking up feeling unrefreshed.
Restless sleep is another common consequence of low GABA levels. Individuals may toss and turn, experience vivid dreams, or wake up feeling anxious and on edge. Over time, chronic sleep deprivation can have a significant impact on overall health and well-being.
GABA and Other Conditions
Beyond anxiety and sleep, GABA's influence extends to a range of other neurological and mental health conditions. While the exact mechanisms are complex and still being researched, imbalances in GABA activity have been implicated in:
- Depression
- Epilepsy
- Chronic Pain
The Link to Neurological Disorders
In Depression, reduced GABA activity in certain brain regions may contribute to symptoms such as low mood, loss of interest, and fatigue. Some studies suggest that enhancing GABA function could be a potential therapeutic strategy for treating depression.
Epilepsy, a neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures, is often associated with an imbalance between excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters. Insufficient GABA activity can lead to excessive neuronal firing, triggering seizures. Some anti-epileptic drugs work by enhancing GABA function.
GABA's role in chronic pain is also being increasingly recognized. GABAergic neurons in the spinal cord help to regulate pain signals, preventing them from reaching the brain. Dysfunction in this system can contribute to chronic pain conditions.
Decoding GABA’s role offers a glimpse into the intricate communication network within our minds, a network where balance is paramount. The dance between excitation and inhibition, governed largely by Glutamate and GABA respectively, dictates the rhythm of our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. Now, let's delve deeper into the specific ways GABA impacts our well-being, exploring its crucial roles in regulating anxiety, promoting restful sleep, and its involvement in various other health conditions.
Factors Influencing GABA Levels: Understanding the Depletion Culprits
While understanding GABA's crucial role is important, it's equally essential to identify the factors that can sabotage its effectiveness. Various elements in our modern lives can negatively impact GABA levels, hindering its calming influence on our brains. Recognizing these "depletion culprits" empowers us to make informed choices to protect and nurture our GABAergic system.
The Vicious Cycle of Stress and GABA
Chronic stress is arguably one of the most pervasive threats to healthy GABA levels. When we experience prolonged periods of stress, our bodies activate the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, leading to the release of cortisol, the primary stress hormone.
While cortisol is essential for managing acute stress, chronic elevation disrupts the delicate balance of neurotransmitters, including GABA. Studies suggest that chronic stress can actually downregulate GABA receptors, making them less responsive to GABA's calming effects. This creates a vicious cycle: stress depletes GABA, leading to increased anxiety and further stress.
This prolonged state of hyperarousal leads to neuronal damage and can significantly impair GABA synthesis. Therefore, managing chronic stress is not just about feeling better; it's about protecting your brain's ability to maintain a healthy balance.
Lifestyle Factors: A Foundation for GABA Health
Beyond stress, our daily lifestyle choices significantly impact GABA levels. Diet, exercise, and sleep habits form the foundation of a healthy GABAergic system.
A diet lacking in essential nutrients can impair GABA synthesis. Specifically, certain amino acids, magnesium, and vitamin B6 are crucial cofactors in the production of GABA. Processed foods, excessive sugar intake, and nutrient deficiencies can disrupt this process.
Regular exercise has been shown to boost GABA levels and improve mood. Physical activity promotes neurogenesis, the growth of new neurons, and can enhance GABA receptor function.
Conversely, inadequate sleep can wreak havoc on GABA levels. Sleep deprivation disrupts neurotransmitter balance, leading to decreased GABA activity and increased anxiety and irritability.
The Complex Relationship Between Substances and GABA
Alcohol and certain pharmaceuticals can exert a powerful, yet often temporary and potentially detrimental, influence on GABA activity.
Alcohol, initially, enhances GABA's effects, leading to feelings of relaxation and reduced anxiety. However, chronic alcohol consumption can lead to GABA receptor downregulation, meaning the brain becomes less sensitive to GABA's effects over time. This can contribute to tolerance, dependence, and withdrawal symptoms, including anxiety and seizures.
Certain pharmaceuticals, such as benzodiazepines, are designed to enhance GABA activity by binding to GABA-A receptors. While these medications can be effective in managing anxiety and insomnia, they also carry a risk of side effects, tolerance, and dependence. Long-term use can lead to GABA receptor downregulation and rebound anxiety upon discontinuation.
It's crucial to approach these substances with caution and understand their potential impact on the GABAergic system. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting or stopping any medication that affects GABA activity.
Ultimately, understanding the factors that deplete GABA empowers us to make conscious choices that support a balanced and resilient brain. By addressing chronic stress, adopting healthy lifestyle habits, and being mindful of the impact of substances, we can nurture our GABAergic system and promote a greater sense of calm and well-being.
Chronic stress erodes our GABA reserves, highlighting the importance of proactive strategies to replenish and support this crucial neurotransmitter. Fortunately, there are numerous natural avenues we can explore to bolster GABA levels, adopting a holistic approach that integrates lifestyle adjustments, dietary enhancements, and the power of physical activity.
Natural Strategies to Boost GABA: A Holistic Approach
The beauty of supporting GABA lies in its accessibility. We aren't necessarily talking about complex medical interventions, but rather conscious choices we can integrate into our daily lives. A holistic approach acknowledges the interconnectedness of mind and body, offering sustainable ways to nurture our brain's natural calming mechanisms.
Lifestyle Modifications: Cultivating Calm from Within
Our daily habits exert a profound influence on neurotransmitter balance. Prioritizing restorative practices can significantly impact GABA levels.
Prioritizing Sleep: The Foundation of GABA Production
Sleep isn't just downtime; it's a crucial period for brain repair and neurotransmitter regulation. During sleep, the brain consolidates information and clears out metabolic waste, processes that are vital for optimal GABA function.
Creating a relaxing bedtime routine signals to your brain that it's time to unwind, preparing it for sleep and, consequently, promoting GABA release.
This routine might include:
- A warm bath or shower.
- Reading a physical book (avoid screens!).
- Gentle stretching or yoga.
- Listening to calming music.
Establishing a consistent sleep schedule, even on weekends, helps regulate your body's natural circadian rhythm, further optimizing GABA production and overall sleep quality.
Stress Management Techniques: Taming the Stress Response
Chronic stress, as we've discussed, is a major GABA antagonist. Actively managing stress is therefore paramount. Mindfulness practices, such as meditation, help cultivate present moment awareness, reducing the reactivity to stressors.
Deep breathing exercises stimulate the parasympathetic nervous system, the body's "rest and digest" system, counteracting the effects of the stress response and promoting GABA release.
Other helpful techniques include:
- Yoga and Tai Chi: Combining physical movement with mindful breathing.
- Spending time in nature: Studies show exposure to nature reduces cortisol levels.
- Engaging in hobbies: Activities that bring joy and relaxation.
Dietary Considerations: Fueling GABA Synthesis
What we eat directly impacts our brain chemistry. Certain nutrients are essential building blocks for GABA synthesis and receptor function.
Key Nutrients for GABA Production
-
Magnesium: This mineral plays a crucial role in GABA receptor function and helps regulate neuronal excitability. Magnesium deficiency has been linked to anxiety and sleep disturbances. Food sources of magnesium include leafy green vegetables, nuts, seeds, and whole grains.
-
Pyridoxine (Vitamin B6): Vitamin B6 is a vital cofactor for the enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD), which converts glutamate into GABA. Without sufficient B6, this conversion process is impaired. Sources of B6 include poultry, fish, bananas, and potatoes.
-
Other Relevant Nutrients: While magnesium and B6 are particularly important, other nutrients contribute to overall brain health and indirectly support GABA function. These include:
- L-Theanine: Found in green tea, L-theanine can increase GABA levels in the brain and promote relaxation without drowsiness.
- Taurine: An amino acid that acts as a GABA agonist, meaning it binds to GABA receptors and enhances their activity.
- Zinc: Important for overall brain function and may play a role in GABA neurotransmission.
It is essential to ensure a balanced diet that provides all the necessary nutrients for optimal GABA synthesis and receptor function.
Exercise: Moving Towards a Calmer Mind
Physical activity is not only beneficial for physical health, but it also has a profound impact on mental well-being and neurotransmitter balance.
The GABA-Boosting Power of Exercise
Studies have shown that regular exercise can increase GABA levels in the brain. Both aerobic exercise (like running or swimming) and resistance training (like weightlifting) have been shown to have a positive effect.
The exact mechanisms by which exercise boosts GABA are still being investigated, but it is thought to involve increased blood flow to the brain, enhanced neuroplasticity, and the release of other beneficial neurochemicals.
The type of exercise doesn't seem to matter as much as consistency. Find an activity you enjoy and can stick to, whether it's a brisk walk in the park, a dance class, or a weightlifting session. The key is to make exercise a regular part of your routine to reap its GABA-boosting benefits.
By embracing these natural strategies, we can proactively cultivate a calmer, more balanced brain, fostering resilience in the face of everyday stressors.
Medical Interventions and GABA: Navigating the Path with Professional Guidance
While lifestyle modifications and dietary adjustments offer natural avenues to support GABA function, certain situations may warrant medical intervention. It's crucial to understand the role of prescription medications targeting the GABA system and the paramount importance of seeking guidance from a qualified healthcare professional.
Prescription Medications: A Double-Edged Sword
Pharmaceutical interventions, particularly benzodiazepines, can significantly enhance GABA activity in the brain. These medications work by binding to GABA-A receptors, amplifying the effects of GABA and promoting a calming, sedative effect. They are often prescribed for managing acute anxiety, insomnia, and seizures.
Benzodiazepines: Benefits and Risks
While effective in providing rapid relief, benzodiazepines come with a significant caveat: the potential for dependence and a range of side effects. Common side effects include drowsiness, dizziness, impaired coordination, and memory problems. Long-term use can lead to tolerance, requiring higher doses to achieve the same effect, and withdrawal symptoms upon discontinuation.
The risks associated with benzodiazepines necessitate careful consideration and close medical supervision. These medications are not a long-term solution for chronic anxiety or sleep disorders. They should be used judiciously, under the guidance of a physician, and for the shortest duration possible.
Beyond Benzodiazepines: Other Pharmaceutical Options
While benzodiazepines are the most well-known GABA-enhancing medications, other pharmaceuticals target the GABA system in different ways. Some medications, such as certain anticonvulsants, can indirectly affect GABA levels or receptor function. These medications are typically prescribed for specific conditions and should only be used under strict medical supervision.
The Indispensable Role of Professional Guidance
Navigating the complexities of GABA-related issues requires the expertise of a healthcare professional. Self-treating with prescription medications or relying solely on anecdotal information can be dangerous and counterproductive.
Why Consult a Healthcare Professional?
A healthcare professional can conduct a thorough evaluation to determine the underlying cause of your symptoms and assess whether medical intervention is necessary. They can also:
- Rule out other potential medical conditions.
- Evaluate your individual risk factors and potential drug interactions.
- Develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.
- Monitor your progress and adjust your treatment as needed.
- Provide guidance on safe and effective ways to taper off medications if necessary.
A Holistic Approach to Well-being
Addressing GABA imbalances is often a multifaceted process that involves lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and, in some cases, medical interventions. A healthcare professional can help you integrate these different approaches to achieve optimal well-being.
It's crucial to remember that prescription medications are just one tool in the toolbox. They should be used in conjunction with other strategies, such as stress management techniques and healthy lifestyle habits, to promote long-term GABA balance and overall health.
In conclusion, while medical interventions can play a role in addressing GABA-related issues, they should always be approached with caution and under the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional. A holistic approach that integrates lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and medical supervision is essential for achieving sustainable well-being.
Video: Unlock GABA: The Key to a Calm, Balanced Brain!
FAQs: Unlock GABA - The Key to a Calm, Balanced Brain!
Here are some frequently asked questions to help you better understand GABA and its role in promoting a calmer, more balanced brain.
What exactly is GABA, and what does it do?
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) is the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. This means its main function is to reduce neuronal excitability throughout the nervous system. By slowing down brain activity, GABA helps promote relaxation and reduce stress.
How does GABA function affect my anxiety levels?
Low levels of GABA function have been linked to increased anxiety and stress. When GABA is insufficient, neurons can become overexcited, leading to feelings of unease, restlessness, and difficulty relaxing. Increasing GABA activity can help mitigate these symptoms.
Can I naturally increase GABA levels in my brain?
Yes, several strategies can naturally increase GABA levels. These include practicing mindfulness, engaging in regular exercise, consuming GABA-rich foods, and ensuring adequate sleep. Certain supplements may also help, but consult with a healthcare professional first.
Is GABA the only neurotransmitter involved in mood and relaxation?
No, while GABA is a crucial neurotransmitter for calming the brain, other neurotransmitters also play significant roles. Serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, among others, all contribute to mood regulation. Achieving a balance among these is key to overall mental wellbeing.